Graphics Rendering: Render Command Encoder
- Creating a Render Pass Descriptor
- Load and Store Actions
- Specifying the Clear Load Action
- Example: Creating a Render Pass Descriptor with Load and Store Actions
- Example: Creating a Render Pass Descriptor for Multisampled Rendering
- Using the Render Pass Descriptor to Create a Render Command Encoder
- Creating and Configuring a Render Pipeline Descriptor
- Creating a Render Pipeline State from a Descriptor
- Configuring Blending in a Render Pipeline Attachment Descriptor
本章描述了如何创建和使用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 和 MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder ,使用它们将graphic render command encode到一个command buffer中。 MTLRenderCommandEncoder describe一个graphic render pipeline,如下图:
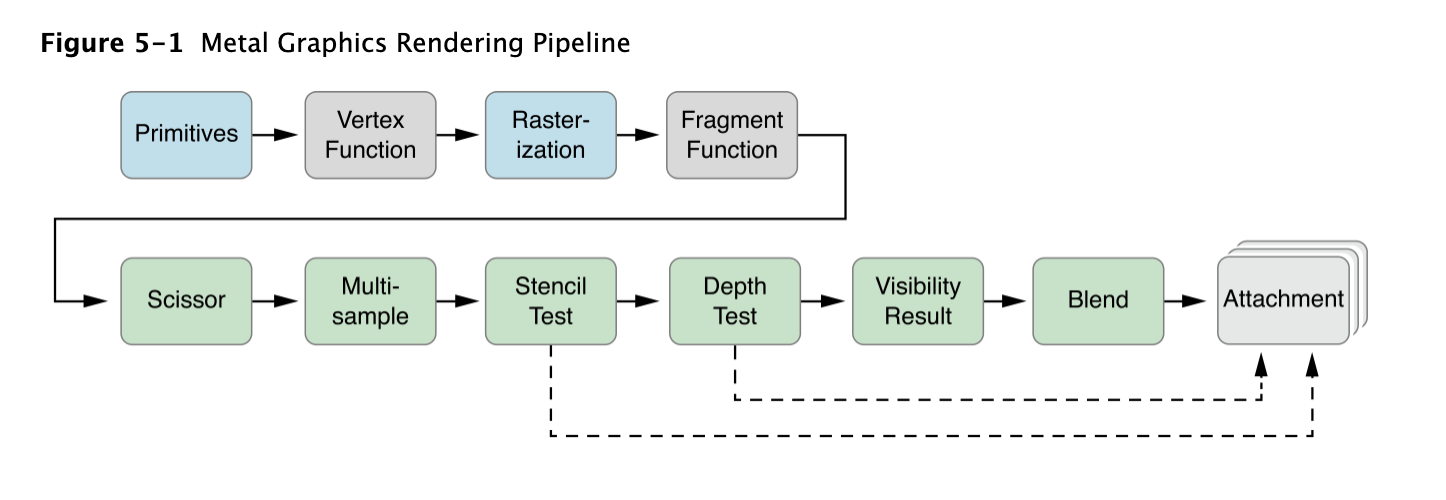
MTLRenderCommandEncoder 提供一个render command encoder。MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 将一个render pass分成若干个独立的 MTLRenderCommandEncoder,每个都可以被分配到不同的thread。然后不同render command encoder中的command 会被以一致的、可预测的顺序连接在一起并执行。
Creating and Using a Render Command Encoder
下面是创建、初始化、使用一个render command encoder的步骤
- 创建一个 MTLRenderPassDescriptor object来指定attachment作为该render pass中command buffer的graphic command 的rt。可以只创建一次 MTLRenderPassDescriptor ,然后每帧重用它。
- 通过 MTLCommandBuffer 的 renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor: 方法以 render pass descriptor 为输入,来创建一个 MTLRenderCommandEncoder
- 创建一个 MTLRenderPipelineState object 来定义一个或者多个dc 的 graphics render pipeline 的 state(包括 shader、blend、multisample、visibility testing)。通过 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setRenderPipelineState 方法来使用这个 render pipeline state 来 绘制primitive
- 设置 texture 、buffer 、samplers 用于 render command encoder
- 调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的方法来制定额外的fixed-function state,包括 depth/stencil state。
- 最终调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的方法去绘制graphics primitives
Creating a Render Pass Descriptor
一个 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 通过一组 attachment 设置 encoded render command 的 rt。render pass descriptor可以包含一组最多4个 color attachment,一个depth attachment,一个 stencil attachment。 renderPassDescriptor 是一个 convenience method 用于创建一个 MTLRenderPassDescriptor object,将 color、depth、stencil attachment设置为默认的attachment state。visibilityResultBuffer 属性指定一个buffer用于device 存放 any samples 通过 depth/stencil test。
每个 attachment,包含即将写入信息的 texture,由一个 attachment descriptor 表现。attachment descriptor 对应的 texture 的 pixel format 必须适合存储 color、depth、stencil。MTLRenderPassColorAttachmentDescriptor 使用一个 color-renderable pixel format。MTLRenderPassDepthAttachmentDescriptor 使用一个 depth-renderable pixel format,比如 MTLPixelFormatDepth32Float。 MTLRenderPassStencilAttachmentDescriptor 使用一个 stencil-renderable pixel format,比如 MTLPixelFormatStencil8
texture中每个像素在device上的内存,并非always match metal framework code 中 texture pixel format对应的尺寸,因为device会添加一些 padding for alignment 或者其它用处。 Metal Feature Set Tables 中介绍了每个pixel format实际使用的内存,以及attachment的数量和尺寸限制
Load and Store Actionsattachment 的 loadAction 和 storeAction 属性指定 render pass 起始处和结尾处的 action(MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 的话,load and store action 发生在整个命令的边界处,而非每个 MTLRenderCommandEncoder object)
loadAction 值包括
- MTLLoadActionClear 指针对 attachment descriptor 的每个pixel,都写入相同的值
- MTLLoadActionLoad 保留 texture中的existing content
- MTLLoadActionDontCare 指在render pass开始的时候,attachment中每个pixel都可以使用任意值
如果在某一帧将会在attachment上写入所有像素,则使用默认load action MTLLoadActionDontCare。MTLLoadActionDontCare 避免了GPU去加载 texture中的现有内容,确保最佳性能。其它情况,可以使用 MTLLoadActionClear 来将attachment之前的内容全部晴空,或者使用 MTLLoadActionLoad 将它们保留下来。 MTLLoadActionClear 也避免了加载texture的现有内容,但是会产生使用纯色填充的消耗。
storeAction 值包括
- MTLStoreActionStore 指将renderpass的最终结果写入 attachment
- MTLStoreActionMultisampleResolve 指将 rt 中multisample data resolve 成 single sample value,将它们存放在 attachment 的 resolveTexture 中,并将attachment的内容设置为 undefine。
- MTLStoreActionDontCare 在renderpass结束后,将attachment设置为 undefine。这个可能会提升性能,因为它使得implementation不去将 render result保存下来。
color attachment中,MTLStoreActionStore为默认操作,因为应用程序大多会在render pass结束的时候讲attachment 的最终颜色保存下来。depth/stencil attachment, MTLStoreActionDontCare 为默认值,因为这些attachment在render pass结束的时候,基本上不需要保存内容
Specifying the Clear Load Action如果attachment descriptor的 loadAction 被设置成了 MTLLoadActionClear,则在render pass开始的时候讲一个clear值写入attachment的所有像素。clear值依赖attachment的类型
- MTLRenderPassColorAttachmentDescriptor 的 clearColor 包含一个 MTLClearColor值,其中包含了四个 double-precision 的 floating-point RGBA component,用于clear该color attachment。MTLClearColorMake 函数通过rgba四个component创建一个 clear color value。默认的clear color是 (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0), or opaque black
- MTLRenderPassDepthAttachmentDescriptor 的 clearDepth 值包含一个 double-precision floating-point 范围在[0.0, 1.0)之间,用于clear depth attachment,默认值为1.0
- MTLRenderPassStencilAttachmentDescriptor 的 clearStencil 值包含一个32-bit unsigned int 用于clear stencil attachment,默认值为0
下面代码创建了一个 render pass descriptor,包含color和depth attachment。首先,创建2个texture,一个使用color-renderable pixel format,另外一个使用depth pixel format。然后使用 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 的 renderPassDescriptor convenience method 创建一个默认的render pass descriptor。然后通过 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 的属性可以访问 color 和 depth attachment。colorattachment[0]包含第一个color attachment对应的texture 和 action,depthAttachment 包含 depth attachment对应的texture 和 action
MTLTextureDescriptor *colorTexDesc = [MTLTextureDescriptor
texture2DDescriptorWithPixelFormat:MTLPixelFormatRGBA8Unorm
width:IMAGE_WIDTH height:IMAGE_HEIGHT mipmapped:NO];
id <.MTLTexture> colorTex = [device newTextureWithDescriptor:colorTexDesc];
MTLTextureDescriptor *depthTexDesc = [MTLTextureDescriptor
texture2DDescriptorWithPixelFormat:MTLPixelFormatDepth32Float
width:IMAGE_WIDTH height:IMAGE_HEIGHT mipmapped:NO];
id <.MTLTexture> depthTex = [device newTextureWithDescriptor:depthTexDesc];
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *renderPassDesc = [MTLRenderPassDescriptor renderPassDescriptor];
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].texture = colorTex;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].storeAction = MTLStoreActionStore;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0);
renderPassDesc.depthAttachment.texture = depthTex;
renderPassDesc.depthAttachment.loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
renderPassDesc.depthAttachment.storeAction = MTLStoreActionStore;
renderPassDesc.depthAttachment.clearDepth = 1.0;
Example: Creating a Render Pass Descriptor for Multisampled Rendering
如果要使用 MTLStoreActionMultisampleResolve ,必须将 texture 设置为一个multisample-type texture,resolveTexture 将包含 multisample resolve后的结果。(如果texture不支持multisample,则multisample resolve action后的结果为未定义)。resolveLevel, resolveSlice, and resolveDepthPlane 将被用于 multisample resolve 操作来指定 multisample texture 的 mipmap level、cube slice、depth plane。大多数情况下,这三个属性将使用默认值。下面代码讲创建一个attachment,然后它的loadAction、storeAction、texture、resolveTexture 属性豆浆支持multisample resolve
MTLTextureDescriptor *colorTexDesc = [MTLTextureDescriptor
texture2DDescriptorWithPixelFormat:MTLPixelFormatRGBA8Unorm
width:IMAGE_WIDTH height:IMAGE_HEIGHT mipmapped:NO];
id <.MTLTexture> colorTex = [device newTextureWithDescriptor:colorTexDesc];
MTLTextureDescriptor *msaaTexDesc = [MTLTextureDescriptor
texture2DDescriptorWithPixelFormat:MTLPixelFormatRGBA8Unorm
width:IMAGE_WIDTH height:IMAGE_HEIGHT mipmapped:NO];
msaaTexDesc.textureType = MTLTextureType2DMultisample;
msaaTexDesc.sampleCount = sampleCount; // must be > 1
id <.MTLTexture> msaaTex = [device newTextureWithDescriptor:msaaTexDesc];
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *renderPassDesc = [MTLRenderPassDescriptor renderPassDescriptor];
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].texture = msaaTex;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].resolveTexture = colorTex;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].storeAction = MTLStoreActionMultisampleResolve;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0);
Using the Render Pass Descriptor to Create a Render Command Encoder
创建了 render pass descritptor并设置好其属性之后,使用MTLCommandBuffer 的 renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor 来创建 render command encoder。参见下面代码
id <.MTLRenderCommandEncoder> renderCE = [commandBuffer
renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:renderPassDesc];
Displaying Rendered Content with Core Animation
Core Animation 定义了 CAMetalLayer Class,用于layer-backed view,content由metal渲染。 CAMetalLayer 展现geometry of content(位置和尺寸)、visual attribute(background color、border、shadow)以及展现 content 的 color attachment resource used by metal。还封装了timeing of content presentation,所以内容将在特定的时间被立即显示。
Core Animation 还定义了 CAMetalDrawable protocol 用于显示。 CAMetalDrawable 继承自 MTLDrawable ,并包含一个 MTLTexture protocol 的 object,所以可以被用作 render command 的destination。 为了渲染到一个 CAMetalLayer object,必须为每个render pass获取一个新的 CAMetalDrawable ,获取到它提供的 MTLTexture,使用这个texture 创建color attachment。和color attachment不同,创建和小会一个depth/stencil attachment 都非常耗。如果需要depth/stencil attachment,创建它们一次,然后在每帧中重用它们。
如下面代码所示,你可以通过 layerclass 方法来设置 CAMetalLayer 作为 custom UIView subclass 的backing layer type。否则,可以使用init方法创建一个 CAMetalLayer ,并将其放在一个已经存在的view中
+ (id) layerClass {
return [CAMetalLayer class];
}
为了显示layer中metal渲染的content,必须从 CAMetalLayer 获取一个 displayable resource(一个 CAMetalDrawable object),然后把它attch到 MTLRenderPassDescriptor上,然后渲染到其texture上。想要完成上述操作,需要首先设置 CAMetalLayer 的属性,获取它提供的 drawable resource,然后在开始新的一帧渲染的时候,调用它的 nextDrawable 方法。如果 CAMetalLayer 的属性没有设置,则 nextDrawable 方法会返回fails。 CAMetalLayer 的下列属性描述 drawable object
- device 属性对应一个 MTLDevice object用于创建该资源
- pixelFormat 属性声明 texture 的pixel format。支持的值为 MTLPixelFormatBGRA8Unorm 和 MTLPixelFormatBGRA8Unorm_sRGB
- drawableSize 属性描述了 texture 的 dimension。为了确保app渲染在display的时候保持在高精度的dimension(在某些设备不需要额外的sampling stage),在计算 layer 的 desired size 的时候 使用target screen 的 nativeScale or nativeBounds 属性
- framebufferOnly 属性描述该texture只被用于 attachment (YES),或者可以被用作 texture smpling 和 pixel read/write 操作(NO)。如果YES,layer object可以对这个texture进行优化用于display。大部分app,这个值建议为YES
- presentsWithTransaction 属性描述 layer的renderd resource 的改动随着 standard Core Animation transaction mechanisms一起更新(YES),还是相对于normal layer update异步更新(NO,默认值)
如果执行 nextDrawable 方法成功,则会返回一个包含下列只读属性的 CAMetalDrawable
- texture 属性对应上述 texture,在创建render pipeline(MTLRenderPipelineColorAttachmentDescriptor)的时候,可以使用它作为attachment
- layer 属性对应用于显示这个 drawable 的 CAMetalLayer object
注意:由于 drawable resource非常有限,所以长时间的帧渲染可能会导致 nextDrawable 方法block CPU thread直到这个方法结束。所以为了避免昂贵的 CPU stall,先执行当前帧所有不需要 drawable resource 的操作,然后再调用 CAMetalLayer object的 nextDrawable 方法。
在渲染结束后,为了显示drawable 的content,你必须通过drawable object 的 present 方法,将其submit到Core Animation。为了同步drawable的现实和command buffer的渲染完成,可以通过 MTLCommandBuffer 的 presentDrawable 和 presentDrawable:atTime: convenience method。这些method使用scheduled handler去调用drawable 的 present 方法,覆盖了大部分 scenarios。presentDrawable:atTime: 方法提供对何时显示drawable的进一步控制。
Creating a Render Pipeline State
为了使用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 去 encode render command,你必须首先指定一个 MTLRenderPipelineState object来指定 dc中的graphics state。render pipeline state是long-lived persistent object,可以created outside render command encoder,cached,然后在多个render command encoders中重复使用。当要使用一个相同的graphics state,重复使用一个之前创建的pipeline state object可以避免昂贵的操作去re-evaluate and translate the specified state to GPU commands
render pipeline state是一个immutable object。为了创建render pipeline state,必须先创建和配置一个mutable MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor object描述 render pipeline state的属性。然后使用该descriptor去创建一个 MTLRenderPipelineState object
Creating and Configuring a Render Pipeline Descriptor
为了创建一个 render pipeline state,首先需要创建一个 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor object,包含描述render pass中用到的 graphics render pipeline state所需要的属性,详见下图。MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor 的 colorAttachments 属性 包含一个 MTLRenderPipelineColorAttachmentDescriptor 数组,每个都代表一个 color attachment state指定该attachment 的 blend operation/blend factor。attachment descriptor 还对应 attachment 的pixel format,必须与render pipeline descriptor 对应 index 的 attachment 的 texture 的pixel format对应,否则就会出现error

配置 color attachment 的时候,需要设置 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor的如下参数
- depthAttachmentPixelFormat 属性必须匹配 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 的 depthAttachment texture 的 pixel format
- stencilAttachmentPixelFormat 属性必须匹配 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 的 stencilAttachment texture 的 pixel format
- vertexFunction or fragmentFunction 属性用于指定 render pipeline state 的 vertex/fragment shader。将 fragmentFunction 设置为 nil,会 disables the rasterization of pixels into the specified color attachment,会被用于 depth-pnly render 或者 从vs 中向一个buffer 输出数据。
- 如果vs由 per-vertex input attribute作为 argument,设置 vertexDescriptor 属性来描述 argument 的 vertext data
- rasterizationEnabled 属性的默认值为 YES。如果值需要graphics pipeline 的 vertex stage(比如gather data transform in a vs),将该属性设置为 NO
- 如果attachment 支持 multisample(attachment是一个 MTLTextureType2DMultisample 类型的texture),可以multiple samples can be created per pixel。为了决定fragment如何combine to provide pixel coverage,使用下列 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor 属性
- sampleCount 属性决定了每个像素的sample数量。当 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 被创建的时候,所有 attachment 对应的 texture 的 sampleCount 属性比喻和这个 sampleCount匹配。如果 attachment 不支持multisampling,则sampleCount 为1,也就是默认值
- 如果 alphaToCoverageEnabled 被设置为 YES,则 colorAttachments[0] 的 fragment output 的 alpha channel 会被读取并用于决定 coverage mask
- 如果 alphaToOneEnabled 被设置为 YES,colorAttachments[0]的 fragment output 的 alpha channel 会被强制设置为 1.0,也就是最大值(其他attachment不受影响)
Creating a Render Pipeline State from a Descriptor
创建了 render pipeline descriptor 并设置了它的属性后,使用它去创建 MTLRenderPipelineState object。由于创建一个 render pipeline state会导致昂贵的graphics state 的 evaluation 并可能产生指定 graphics shader 的编译。建议使用block 或者一个异步方法来执行这种工作来获取最好的性能
- 同步的创建这个renderpipeline state object,调用 MTLDevice 的 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:error: 或者 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:options:reflection:error: 方法。这些方法会block当前的thread,这个时候metal evaluates descriptor 的guaphics state information以及编译shader 去创建pipeline state object
- 异步的创建 render pipeline state object,调用 MTLDevice 的 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:completionHandler: 或者 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:options:completionHandler: 方法。这些方法会直接返回=metal会异步的evaluates descriptor 的guaphics state information以及编译shader 去创建pipeline state object,然后调用 completion handler 去提供新的 MTLRenderPipelineState object。
创建 MTLRenderPipelineState 的时候可以选择同时创建 reflection data 展示 pipeline shader function 的detail 和argument。对应的方法是 MTLDevice 的 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:options:reflection:error: 和 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:options:completionHandler: 。如果不用的话,尽量不要生成 reflection data。
创建了 MTLRenderPipelineState 后,调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setRenderPipelineState: 方法去对 command encoder 设置 render pipelinbe state 用于渲染。
下面代码创建了一个 render pipeline state object 叫做 pipeline
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor *renderPipelineDesc =
[[MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor alloc] init];
renderPipelineDesc.vertexFunction = vertFunc;
renderPipelineDesc.fragmentFunction = fragFunc;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].pixelFormat = MTLPixelFormatRGBA8Unorm;
// Create MTLRenderPipelineState from MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor
NSError *errors = nil;
id <.MTLRenderPipelineState> pipeline = [device
newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:renderPipelineDesc error:&errors];
assert(pipeline && !errors);
// Set the pipeline state for MTLRenderCommandEncoder
[renderCE setRenderPipelineState:pipeline];
vertFunc 和 fragFunc 是 shader functions,作为 render pipeline state descriptor renderPipelineDesc 的属性。调用 MTLDevice 的 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:error: 方法同步的使用pipeline state descriptor 去创建 render pipeline state object。调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setRenderPipelineState: 方法来指定 MTLRenderPipelineState object 用于 render command encoder。
注意:MTLRenderPipeline object 创建起来很昂贵,所以当你需要用相同的graphics state 的时候重用它。
Configuring Blending in a Render Pipeline Attachment Descriptor
blend 使用一个高度配置化的 blend operation来混合 fragment function 的输出(source)和attachment 上的pixel value(destination)。blend operation 决定source 和 destination 如何根据blend factor 混合
通过设置 MTLRenderPipelineColorAttachmentDescriptor 的属性,来配置 color attachment 的 blend
设置 blendingEnabled 属性为 YES 来开启 blend。默认为关闭
writeMask 属性指定哪些color channel 被 blend。默认值 MTLColorWriteMaskAll 允许所有 color channel被 blend
rgbBlendOperation and alphaBlendOperation 分别用 MTLBlendOperation 值设置 fragment data 中 RGB 和 A 的blend operation,默认情况下两者均为 MTLBlendOperationAdd
sourceRGBBlendFactor, sourceAlphaBlendFactor, destinationRGBBlendFactor, and destinationAlphaBlendFactor 设置 source 和 destination 的 blend factor
Understanding Blending Factors and Operations有四个blend factor 是blend color 常数值:MTLBlendFactorBlendColor, MTLBlendFactorOneMinusBlendColor, MTLBlendFactorBlendAlpha, and MTLBlendFactorOneMinusBlendAlpha。调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setBlendColorRed:green:blue:alpha: 方法来指定这些 blend factor 将要用到的 color 和 alpha 值。
一些 blend operation 将 fragment value 乘以 source MTLBlendFactor(缩写为 SBF),将 destination value 乘以 destination blend factor(DBF),然后使用 MTLBlendOperation 值指示的算术组合来计算。(如果 blend operation 是 MTLBlendOperationMin or MTLBlendOperationMax,则 SBF 和 DBF blend factor 将被忽略)。比如 rgbBlendOperation 和 alphaBlendOperation 都为 MTLBlendOperationAdd 的时候执行下列操作
- RGB = (Source.rgb * sourceRGBBlendFactor) + (Dest.rgb * destinationRGBBlendFactor)
- Alpha = (Source.a * sourceAlphaBlendFactor) + (Dest.a * destinationAlphaBlendFactor)
默认的 blend 操作为 source 完全覆盖 destination。这个操作相当于设置 sourceRGBBlendFactor and sourceAlphaBlendFactor 为 MTLBlendFactorOne,destinationRGBBlendFactor and destinationAlphaBlendFactor 设置为 MTLBlendFactorZero。用公式来描述是:
- RGB = (Source.rgb * 1.0) + (Dest.rgb * 0.0)
- A = (Source.a * 1.0) + (Dest.a * 0.0)
还有一个常见的 blend operation,用source alpha 来决定保留多少 destination color,用公式来描述是:
- RGB = (Source.rgb * 1.0) + (Dest.rgb * (1 - Source.a))
- A = (Source.a * 1.0) + (Dest.a * (1 - Source.a))
下列代码描述了一个自定义的blend 配置,使用 MTLBlendOperationAdd,source blend factor 为 MTLBlendFactorOne , destination blend factor 为 MTLBlendFactorOneMinusSourceAlpha 。colorAttachments[0]是使用了上述 blend 配置的 MTLRenderPipelineColorAttachmentDescriptor object
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor *renderPipelineDesc =
[[MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor alloc] init];
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].blendingEnabled = YES;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].rgbBlendOperation = MTLBlendOperationAdd;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].alphaBlendOperation = MTLBlendOperationAdd;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].sourceRGBBlendFactor = MTLBlendFactorOne;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].sourceAlphaBlendFactor = MTLBlendFactorOne;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].destinationRGBBlendFactor =
MTLBlendFactorOneMinusSourceAlpha;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].destinationAlphaBlendFactor =
MTLBlendFactorOneMinusSourceAlpha;
NSError *errors = nil;
id <.MTLRenderPipelineState> pipeline = [device
newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:renderPipelineDesc error:&errors];
Specifying Resources for a Render Command Encoder
本节中介绍的 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 方法用于指定vs和ps中使用的 argument。vs和ps由 MTLRenderPipelineState 的 vertexFunction and fragmentFunction 属性指定。如下图所示,这些方法将 shader resource (buffer、texture、samplers)对应 render command encoder 的 argument table index(atIndex)
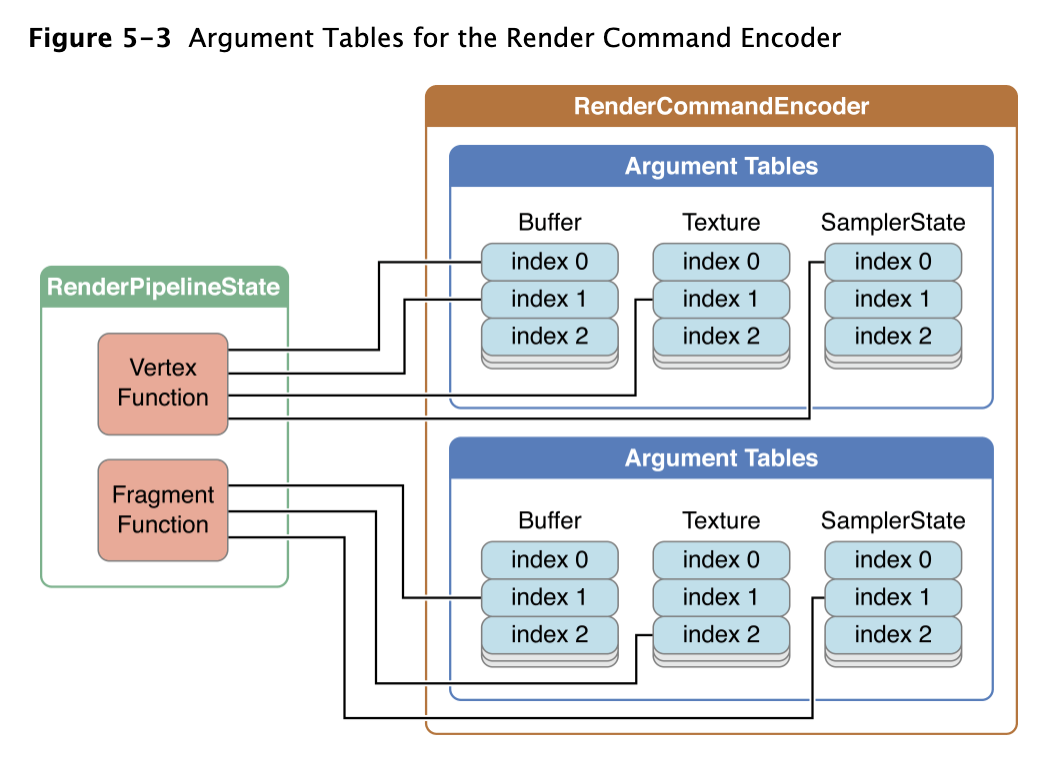
下列的 setVertex* 函数将一个或者多个 resource 对应到 vs function 对应的argument
- setVertexBuffer:offset:atIndex:
- setVertexBuffers:offsets:withRange:
- setVertexTexture:atIndex:
- setVertexTextures:withRange:
- setVertexSamplerState:atIndex:
- setVertexSamplerState:lodMinClamp:lodMaxClamp:atIndex:
- setVertexSamplerStates:withRange:
- setVertexSamplerStates:lodMinClamps:lodMaxClamps:withRange:
下列的 setFragment* 函数将一个或者多个 resource 对应到 ps function 对应的argument
- setFragmentBuffer:offset:atIndex:
- setFragmentBuffers:offsets:withRange:
- setFragmentTexture:atIndex:
- setFragmentTextures:withRange:
- setFragmentSamplerState:atIndex:
- setFragmentSamplerState:lodMinClamp:lodMaxClamp:atIndex:
- setFragmentSamplerStates:withRange:
- setFragmentSamplerStates:lodMinClamps:lodMaxClamps:withRange:
buffer argument table 的上限是31,texture argument table 的上限是31,sampler state argument table 的上限是16
metal shading language source code 中用于指定 resource location 的 attribute qualifier 必须和metal framework method 中的 argument table indices对应。下面代码为 vs 定义了2个buffer(posBuf和texCoordBuffer),index 为 0 和 1。
[renderEnc setVertexBuffer:posBuf offset:0 atIndex:0];
[renderEnc setVertexBuffer:texCoordBuf offset:0 atIndex:1];
下面代码的function signature 使用 attribute qualifiers buffer(0)和buffer(1)对应arguments
vertex VertexOutput metal_vert(float4 *posData [[ buffer(0) ]],
float2 *texCoordData [[ buffer(1) ]])
类似的,下面代码为 ps 创建了一个buffer、texture、sampler(fragmentColorBuf、shadeTex、sampler),index 为 0
[renderEnc setFragmentBuffer:fragmentColorBuf offset:0 atIndex:0];
[renderEnc setFragmentTexture:shadeTex atIndex:0];
[renderEnc setFragmentSamplerState:sampler atIndex:0];
下面代码的function signature 使用 attribute qualifiers buffer(0)、texture(0)和sampler(0)对应arguments
fragment float4 metal_frag(VertexOutput in [[stage_in]],
float4 *fragColorData [[ buffer(0) ]],
texture2d<.float> shadeTexValues [[ texture(0) ]],
sampler samplerValues [[ sampler(0) ]] )
Vertex Descriptor for Data Organization
metal framework code 中,可以只有一个 MTLVertexDescriptor 用于所有的 pipeline state,用于描述穿入 vertex shader function 的数据,以及 shading language 和 frameworke code 之间共享的 resource location information
在 metal shading language code 中,per- vertex input(比如 int/float-point 类型的 scalar、vector)可以被组织放入一个结构体,这样可以通过一个拥有 stage_in attribute qualifier 的 argument 声明,比如下面例子中 vertexMath 函数 的 VertexInput 结构体。该结构体的每个值都有一个 qualifier attribute(index),用于对应 vertex attribute argument table 中的 index
struct VertexInput {
float2 position [[ attribute(0) ]];
float4 color [[ attribute(1) ]];
float2 uv1 [[ attribute(2) ]];
float2 uv2 [[ attribute(3) ]];
};
struct VertexOutput {
float4 pos [[ position ]];
float4 color;
};
vertex VertexOutput vertexMath(VertexInput in [[ stage_in ]])
{
VertexOutput out;
out.pos = float4(in.position.x, in.position.y, 0.0, 1.0);
float sum1 = in.uv1.x + in.uv2.x;
float sum2 = in.uv1.y + in.uv2.y;
out.color = in.color + float4(sum1, sum2, 0.0f, 0.0f);
return out;
}
对应使用 stage_in qualifier 的 shader function input,需要定义一个 MTLVertexDescriptor object,然后将其设置为 MTLRenderPipelineState 的 vertexDescriptor 属性。 MTLVertexDescriptor 有2个属性: attribute 和 layouts
MTLVertexDescriptor 的 attribute 属性是一个 MTLVertexAttributeDescriptorArray object 定义了vertex attribute 的每个属性是如何在buffer中组织,并映射到 vertex function argument 中。attribute 属性支持将多个 attribute(比如 vertex coordinate、surface normal、texture coordinate)放在同一个buffer中。shading language 中的顺序不一定需要按照 framework code 的buffer中的顺序。每个 vertex attribute descirptor都具备以下属性,用于提供vs function information 去 定位 和 load argument data。
- bufferIndex,对应 buffer argument table 的 index 指定将要访问哪个 MTLBuffer。
- format,指定数据在framework code 中如何被解读。如果 data type 不匹配,则可能会发生类型转换 或者 expanded。比如,如果 shading language 中类型为 half4,framework 中 format 为 MTLVertexFormatFloat2,当这个数据被用于 vs 的 argument 的时候,可能会从 float 转换成 half,然后 expanded from 2个元素 to 4个元素(后面两个元素为0.0,1.0)
- offset,表明数据从vertex 的哪一位开始
下面展示了 Metal framework code 中的 MTLVertexAttributeDescriptorArray 实现了一个 buffer 对应 shading language vs vertexMath 的输入
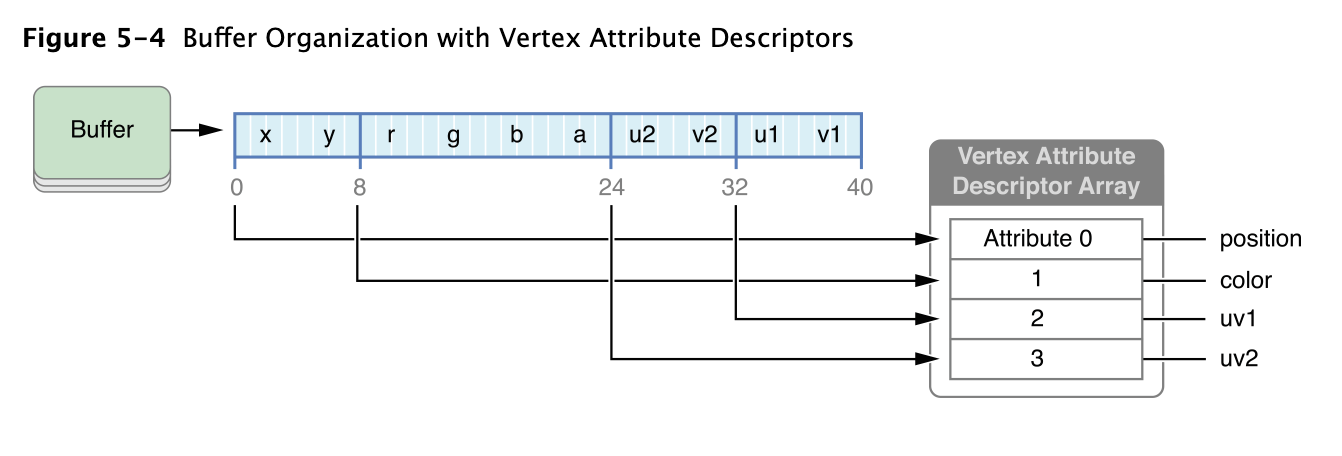
下面代码为对应上述图片的 metal framework code
id <.MTLFunction> vertexFunc = [library newFunctionWithName:@"vertexMath"];
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor* pipelineDesc =
[[MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor alloc] init];
MTLVertexDescriptor* vertexDesc = [[MTLVertexDescriptor alloc] init];
vertexDesc.attributes[0].format = MTLVertexFormatFloat2;
vertexDesc.attributes[0].bufferIndex = 0;
vertexDesc.attributes[0].offset = 0;
vertexDesc.attributes[1].format = MTLVertexFormatFloat4;
vertexDesc.attributes[1].bufferIndex = 0;
vertexDesc.attributes[1].offset = 2 * sizeof(float); // 8 bytes
vertexDesc.attributes[2].format = MTLVertexFormatFloat2;
vertexDesc.attributes[2].bufferIndex = 0;
vertexDesc.attributes[2].offset = 8 * sizeof(float); // 32 bytes
vertexDesc.attributes[3].format = MTLVertexFormatFloat2;
vertexDesc.attributes[3].bufferIndex = 0;
vertexDesc.attributes[3].offset = 6 * sizeof(float); // 24 bytes
vertexDesc.layouts[0].stride = 10 * sizeof(float); // 40 bytes
vertexDesc.layouts[0].stepFunction = MTLVertexStepFunctionPerVertex;
pipelineDesc.vertexDescriptor = vertexDesc;
pipelineDesc.vertexFunction = vertFunc;
MTLVertexDescriptor 的 attributes 属性中对应的每个 MTLVertexAttributeDescriptor 对应 shader function 中的 VertexInput 结构体。attributes[1].bufferIndex = 0 表示使用 argument table 中 index 0 的buffer(这个例子中,每个 MTLVertexAttributeDescriptor 都有一个相同的 bufferIndex,所以全部都对应相同的 vertex buffer,也就是argument table中index 0的buffer。)offset 指定数据的偏移,所以attributes[1].offset = 2 * sizeof(float) 的位置是buffer偏移8 bytes后的数据。format 对应 shader function 中的 data type,所以 attributes[1].format = MTLVertexFormatFloat4 指定使用 4 float-point value
MTLVertexDescriptor 的 layouts 属性 为 MTLVertexBufferLayoutDescriptorArray。layouts 中的每个 MTLVertexBufferLayoutDescriptor 表明在Metal渲染primitive 的时候 vertex attribute data是如何从argument table中对应的MTLBuffer中获取。 MTLVertexBufferLayoutDescriptor 的 stepFunction 属性决定是针对每个顶点获取数据,还是一定数量instance,还是只活去一次。如果 stepFunction 被设置为以一定数量instance为单位活去数据,则 MTLVertexBufferLayoutDescriptor 的 stepRate 属性决定多少数量的instance 为单位。 stride 属性决定了两个 vertex的数据间距,以bytes为单位
下图定义了 MTLVertexBufferLayoutDescriptor 对应上面的代码,layouts[0] 定义了如何从 buffer argument table 中 index 0 的buffer 中获取数据。layouts[0].stride 表示 2个vertex 的数据间距为 40 bytes。layouts[0].stepFunction 为 MTLVertexStepFunctionPerVertex,表示在渲染的时候,数据以vertex为单位获取数据,如果 stepFunction 为 MTLVertexStepFunctionPerInstance,则 stepRate 属性用于决定多少个 instance 获取一次数据。比如 stepRate 为1,data按照每个instance 获取数据,如果 stepRate 为2,则2个instance获取一次数据。
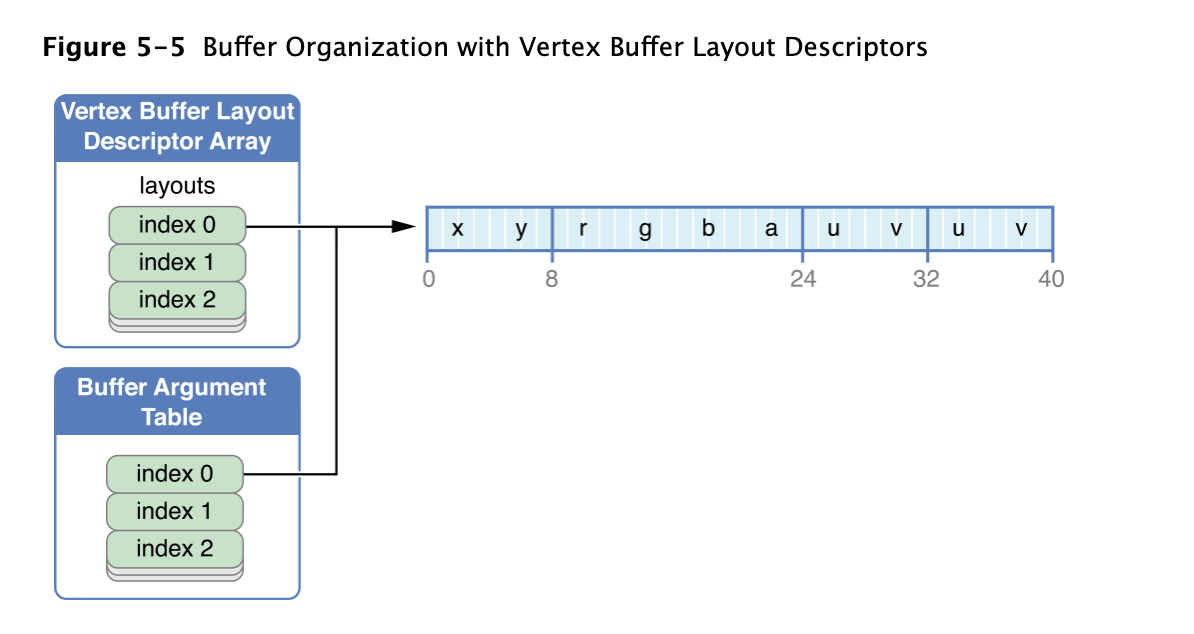
Performing Fixed-Function Render Command Encoder Operations
使用 MTLRenderCommandEncode 的下列方法来设置 fixed-function graphics state value
- setViewport: 从虚拟的3d 世界投影到屏幕坐标系的一个区域。viewport 是3D,所以包含 depth。
- setTriangleFillMode: 设置triangle 和 triangle strip primitive 的 rasterize 方式。以line的方式(MTLTriangleFillModeLines)或者filled triangles(MTLTriangleFillModeFill,默认值)的方式。
- setCullMode: and setFrontFacingWinding: 在一起决定如何执行cull。可以通过culling为一些geometric models执行 hidden surface removal,比如一个通过filled triangle渲染的定向球。(当所有primitives统一的按照顺时针或者逆时针渲染,则被称为 定向)
- setFrontFacingWinding: 指出 vertex 按照顺时针(MTLWindingClockwise,默认值)还是逆时针(MTLWindingCounterClockwise)渲染为 front-face
- setCullMode: 决定是否culling(如果不culling,则MTLCullModeNone),以及如何culling(MTLCullModeFront or MTLCullModeBack)
使用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的下面方法去 encode fixed-function state change command
- setScissorRect: 指定了一个 2D scissor 矩形。scissor 矩形 外面的 fragment 将会被discard
- setDepthStencilState: 设置 depth/stenci test state
- setStencilReferenceValue: 设置 stencil reference value
- setDepthBias:slopeScale:clamp: 设置一个纠正值用于对比 shadowmap 和 fragment shader 输出的 depth value
- setVisibilityResultMode:offset: 决定是否要检测是否有sample通过了depth/stencil test。如果设置为 MTLVisibilityResultModeBoolean,则如果有任意 sample 通过了depth/stencil test,则会将 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 的 visibilityResultBuffer 属性 对应的buffer 写入一个非零值。可以通过这个来执行 occlusion test。方法是:绘制一个bounding box,假如没有 sample pass,则可以断定该bounding box中的object都被挡住了,也就不需要被渲染
- setBlendColorRed:green:blue:alpha: 指定 blend color and alpha 的常数值
Working with Viewport and Pixel Coordinate Systems
metal 定义了它的 Normalized Device Coordinate(NDC)系统为一个2*2*1的cube,中心点为(0,0,0.5)。左下角的x和y为-1,右上角的x和y为+1
viewport指定了NDC到window coordinates的变换矩阵。Metal viewport 是一个 3D transformation,由 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setViewport: 方法定义。window coordinate 的原始点为左下角
在metal中,pixel 中心点会进行(0.5,0.5)的偏移。比如原始点像素的中心点为(0.5,0.5),其右侧相邻像素的中心点为(1.5,0.5)。这个也适用于texture
Performing Depth and Stencil Operations
depth/stencil operation 是 fragment operation,以下面方式指定
- 定义一个 MTLDepthStencilDescriptor object,包含depth/stencil state。一个 MTLDepthStencilDescriptor 可能对应1个或者2个 MTLStencilDescriptor object用于 front-facing/back-facing primitive
- 调用 MTLDevice 的 newDepthStencilStateWithDescriptor 方法根据 depth/stencil state descriptor 创建一个 MTLDepthStencilState 对象
- 调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setDepthStencilState: 方法,使用 MTLDepthStencilState 设置 depth/stencil state
- 如果使用了 stencil test,则调用 setStencilReferenceValue 方法来制定 stencil reference value
如果开启 depth test,render pipeline state 必须包含一个 depth attachment 去支持 depth value 的写入。为了支持 stencil test,render pipeline state 必须包含一个 stencil attachment
如果想要改变depth/stencil state,可以重用 state descriptor object,修改它的值以创建更多的 state object
注意:在shader中采样一个 depth-format texture的时候,implement shader 中的 sample operation不使用 MTLSamplerState
MTLDepthStencilDescriptor 的如下属性设置 depth/stencil state
- 开启 depth value 的写入,将 depthWriteEnabled 设置为 YES
- depthCompareFunction 指定如何进行depth test。如果一个fragment 的depth test失败,则该fragment 将被丢弃。比如最常见的 MTLCompareFunctionLess 将对比 刚计算出来的fragment与之前保存的fragment,如果从观察者角度来看,前者更远,则depth test 失败。也就是说,该fragment被之前的depth挡住了
- frontFaceStencil and backFaceStencil 分别针对 front- and back-facing primitives 指定了2个 MTLStencilDescriptor。如果想要针对 front- and back-facing primitives 使用相同的 stencil state,可以针对 frontFaceStencil and backFaceStencil 设置相同的 MTLStencilDescriptor 。如果想明确的关闭其中一个或者两者的stencil test,将相应的属性设置为nil,也就是默认值
没有必要显式的关闭stencil state。metal决定是否开启stencil test是基于stencil descriptor 是否被配置了一个合法的stencil operation
下面代码展示了创建和使用一个 MTLDepthStencilDescriptor 并创建 MTLDepthStencilState object。然后被用于 render command encoder。在这个例子中,front-facing primitive 的stencil state是通过 depth/stencil state descriptor 的 frontFaceStencil property 设置。front-facing primitive 的stencil test 被显式关闭了
MTLDepthStencilDescriptor *dsDesc = [[MTLDepthStencilDescriptor alloc] init];
if (dsDesc == nil)
exit(1); // if the descriptor could not be allocated
dsDesc.depthCompareFunction = MTLCompareFunctionLess;
dsDesc.depthWriteEnabled = YES;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.stencilCompareFunction = MTLCompareFunctionEqual;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.stencilFailureOperation = MTLStencilOperationKeep;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.depthFailureOperation = MTLStencilOperationIncrementClamp;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.depthStencilPassOperation =
MTLStencilOperationIncrementClamp;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.readMask = 0x1;
dsDesc.frontFaceStencil.writeMask = 0x1;
dsDesc.backFaceStencil = nil;
id <.MTLDepthStencilState> dsState = [device
newDepthStencilStateWithDescriptor:dsDesc];
[renderEnc setDepthStencilState:dsState];
[renderEnc setStencilReferenceValue:0xFF];
MTLStencilDescriptor 的下列属性定义了 stencil test
- readMask 是一个 bitmask,GPU 在对比 stencil reference value 和 stored stencil value 的时候,先与mask按位与之后,再做对比
- writeMask 是一个 bitmask,限制当前 stencil operation 写入 stencil attachment 的指定几位
- stencilCompareFunction 指定如何对 fragment 进行 stencil test。在上述代码中,stencil 对比函数为 MTLCompareFunctionEqual,也就是当 masked reference value 等于 masked stencil value 的时候 stencil test 通过
- stencilFailureOperation, depthFailureOperation, and depthStencilPassOperation 定义了在三中不同情况下,如何处理stencil attachment 的值:stencil test 失败(stencil value 不变 MTLStencilOperationKeep),stencil test 通过 depth test 失败,stencil 和 depth test 都通过(stencil value + 1, 除非已经达到最大值 MTLStencilOperationIncrementClamp)。
Drawing Geometric Primitives
当 pipeline state 和 fixed-function state 都配置好后,可以调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 方法去渲染 geometric primitive。这些方法 reference resource(比如包含 vertex coordinate、texture coordinate、surface normal以及其他数据的 buffer)去执行之前定义在 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 中包含 shader function 和其他 state 的 pipeline
- drawPrimitives:vertexStart:vertexCount:instanceCount: 渲染 instanceCount 个 instance,vertex data是连续 array 元素,开始于 vertexStart 的第一个数组元素,结束于第 vertexStart + vertexCount - 1 个数组元素
- drawPrimitives:vertexStart:vertexCount: 和上个方法的区别就是 instanceCount 为 1
- drawIndexedPrimitives:indexCount:indexType:indexBuffer:indexBufferOffset:instanceCount: 渲染 instanceCount 个 instance,index list 在 MTLBuffer object indexBuffer中。indexCount 决定 index 的数量,index list 开始于 indexBuffer 中 indexBufferOffset 偏移处。indexBufferOffset 必须是一个 index 尺寸的整数倍,尺寸由 indexType 决定
- drawIndexedPrimitives:indexCount:indexType:indexBuffer:indexBufferOffset: 和上个方法的区别就是 instanceCount 为 1
上述的所有渲染方法的第一个输入值,都通过一个 MTLPrimitiveType 值决定primitive type。其他输入值决定用哪些顶点来组成 primitive。所有这些方法,输入值 instanceStart 决定第一个渲染的 instance,instanceCount 决定渲染多少个 instance。
正如上述讨论的, setTriangleFillMode: 决定三角形是按照填充的方式渲染还是只渲染 wireframe, setCullMode: and setFrontFacingWinding: 决定渲染时如何进行 GPU cull triangle。
当渲染一个point primitive 的时候,vs的shader language coder必须包含 point_size attribute,否则point size 为未定义
当按照 flat shading 的方式渲染三角形的时候,第一个vertex (也被称为 provoking vertex)的属性将被用于整个三角形。vs的shader language code也必须包含 flat interpolation qualifier
更多 metal shading language attribute and qualifier,参考Metal Shading Language Guide.
Ending a Rendering Pass
结束一个render pass,需要调用 render command encoder 的 endEncoding 函数。当结束了之前 command encoder 后,可以创建一个新的任意类型的command encoder 去将更多的 command encode 到 command buffer 中
Code Example: Drawing a Triangle
根据下列步骤合代码,描述一个渲染三角形的基本步骤
- 创建一个 MTLCommandQueue ,并用它创建一个 MTLCommandBuffer
- 创建一个 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 并制定一系列 attachment,作为command buffer中render command 的 destination。在这个例子中,只有第一个 color attachment 被设置和使用(currentTexture 被创建并包含一个 MTLTexture,用于 color attachment)。然后使用这个 MTLRenderPassDescriptor 去创建一个新的 MTLRenderCommandEncoder
- 创建2个 MTLBuffer ,posBuf 和 colBuf,调用 newBufferWithBytes:length:options:将vertex coordinate (posData)和 vertex color data(colData)传入buffer
- 调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setVertexBuffer:offset:atIndex: 方法两次,去指定coordinated 和color。其中输入参数 atIndex 对应 vs的source code 中的 attribute buffer(atIndex)
- 创建一个 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor 并在其中赋值 vs和ps
- 使用 source code (proSrc,一个包含Metal shader source code 的 string)创建一个MTLLibrary
- 调用 MTLLibrary 的 newFunctionWithName: 创建 MTLFunction vertFunc 对应函数 hello_vertex,创建 MTLFunction fragFunc 对应函数 hello_fragment
- 使用这些 MTLFunction 设置 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor 的 vertexFunction and fragmentFunction 属性
- 使用 MTLDevice 的 newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:error: 或者类似的方法,通过 MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor 创建 MTLRenderPipelineState。然后调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setRenderPipelineState: 将创建的pipeline state 用于渲染
- 调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 drawPrimitives:vertexStart:vertexCount: 方法渲染一个filled triangle(MTLPrimitiveTypeTriangle))
- 调用 endEncoding 方法来结束这个render pass 的 encoding。然后调用 MTLCommandBuffer 的commit 方法去在device 上执行这些命令
id <.MTLDevice> device = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice();
id <.MTLCommandQueue> commandQueue = [device newCommandQueue];
id <.MTLCommandBuffer> commandBuffer = [commandQueue commandBuffer];
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *renderPassDesc
= [MTLRenderPassDescriptor renderPassDescriptor];
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].texture = currentTexture;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.0,1.0,1.0,1.0);
id <.MTLRenderCommandEncoder> renderEncoder =
[commandBuffer renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:renderPassDesc];
static const float posData[] = {
0.0f, 0.33f, 0.0f, 1.f,
-0.33f, -0.33f, 0.0f, 1.f,
0.33f, -0.33f, 0.0f, 1.f,
};
static const float colData[] = {
1.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f,
0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f,
0.f, 0.f, 1.f, 1.f,
};
id <.MTLBuffer> posBuf = [device newBufferWithBytes:posData
length:sizeof(posData) options:nil];
id <.MTLBuffer> colBuf = [device newBufferWithBytes:colorData
length:sizeof(colData) options:nil];
[renderEncoder setVertexBuffer:posBuf offset:0 atIndex:0];
[renderEncoder setVertexBuffer:colBuf offset:0 atIndex:1];
NSError *errors;
id <.MTLLibrary> library = [device newLibraryWithSource:progSrc options:nil
error:&errors];
id <.MTLFunction> vertFunc = [library newFunctionWithName:@"hello_vertex"];
id <.MTLFunction> fragFunc = [library newFunctionWithName:@"hello_fragment"];
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor *renderPipelineDesc
= [[MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor alloc] init];
renderPipelineDesc.vertexFunction = vertFunc;
renderPipelineDesc.fragmentFunction = fragFunc;
renderPipelineDesc.colorAttachments[0].pixelFormat = currentTexture.pixelFormat;
id <.MTLRenderPipelineState> pipeline = [device
newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:renderPipelineDesc error:&errors];
[renderEncoder setRenderPipelineState:pipeline];
[renderEncoder drawPrimitives:MTLPrimitiveTypeTriangle
vertexStart:0 vertexCount:3];
[renderEncoder endEncoding];
[commandBuffer commit];
上述代码中 ,MTLFunction 表示名为 hello_vertex 的shader function。MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 setVertexBuffer:offset:atIndex: 函数用于指定 vertex resource(这个例子中是2个buffer),也作为argument传入 hello_vertex。setVertexBuffer:offset:atIndex: 的 atIndex 对应 vs source code 中的 attribute buffer(atIndex),下面为对应的shader code
vertex VertexOutput hello_vertex(
const global float4 *pos_data [[ buffer(0) ]],
const global float4 *color_data [[ buffer(1) ]])
{
...
}
Encoding a Single Rendering Pass Using Multiple Threads
在一些情况下,app的性能可能会受限于一个 render pass 在单一CPU encode command 的 workload。如果拆成多个render pass encoded在多个 cpu thread可能也会对性能产生影响,因为每个 render pass 都需要设置 load/store action来保留 render target content
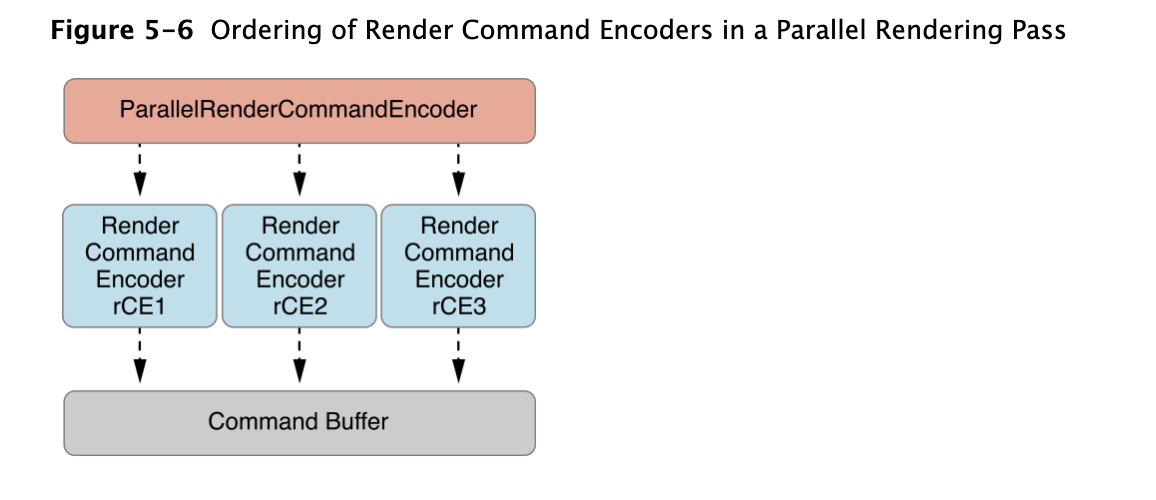
Instead,使用 MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 对应多个 subordinate MTLRenderCommandEncoder object,共享相同的 command buffer 和 render pass descriptor。parallel render command encoder 确保 attachment load and store action 之发生在整个render pass 的开始和结束处,并非每个 subordinate render command encoder 的开始和结束处。通过这个架构,可以将每个 MTLRenderCommandEncoder object 并行的放在自己的先生,得到一个安全高效的方案
使用 MTLCommandBuffer 的 parallelRenderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor: 方法来创建 parallel render command encoder。在每个cpu thread 调用MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 的 renderCommandEncoder 方法一次,去创建 subordinate render command encoder。同一个parallel render command encoder 创建的所有的 subordinate render command encoder 将 command encode 到同一个 command buffer 中。command encode到command buffer 的顺序,按照 render command encoder创建的顺序。调用 MTLRenderCommandEncoder 的 endEncoding 方法来结束 指定 render command encoder 的encoding。当parallel render command encoder对应的所有render command encoder 都encoding后,调用 MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 来结束 render pass
下面代码表示用 MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder 创建3个 MTLRenderCommandEncoder object:rCE1,rCE2,rCE3
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *renderPassDesc
= [MTLRenderPassDescriptor renderPassDescriptor];
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].texture = currentTexture;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
renderPassDesc.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);
id <.MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder> parallelRCE = [commandBuffer
parallelRenderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:renderPassDesc];
id <.MTLRenderCommandEncoder> rCE1 = [parallelRCE renderCommandEncoder];
id <.MTLRenderCommandEncoder> rCE2 = [parallelRCE renderCommandEncoder];
id <.MTLRenderCommandEncoder> rCE3 = [parallelRCE renderCommandEncoder];
// not shown: rCE1, rCE2, and rCE3 call methods to encode graphics commands
//
// rCE1 commands are processed first, because it was created first
// even though rCE2 and rCE3 end earlier than rCE1
[rCE2 endEncoding];
[rCE3 endEncoding];
[rCE1 endEncoding];
// all MTLRenderCommandEncoders must end before MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder
[parallelRCE endEncoding];
command encoder 调用 endEncoding 的顺序与 command encoded和appended 到 MTLCommandBuffer 的顺序无关。MTLParallelRenderCommandEncoder中,MTLCommandBuffer 中的命令顺序只与 subordinate render command encoder 创建的顺序有关,如下图
本节教程就到此结束,希望大家继续阅读我之后的教程。
谢谢大家,再见!
原创技术文章,撰写不易,转载请注明出处:电子设备中的画家|王烁 于 2022 年 4 月 25 日发表,原文链接(http://geekfaner.com/shineengine/blog50_MetalProgrammingGuide_5.html)